From the evolution of the human race, countless scientific endeavors have been carried out for comfortable and luxurious lifestyles. The inventions and discoveries have come up with the promise to make our life beautiful. We look for comfort, joy, and security by exploiting/harnessing natural as well as man-made objects. Human desires are endless; therefore, scientific exploration/expedition has been paramount in the last few decades.
The outcome is we are on the verge of witnessing the extinction of fossil fuels and other natural resources. The more alarming fact is that the planet is drastically polluted. Both the issues have been addressed, and an ecofriendly solution has been proposed by scientists using a technology coined as “Green Photonics.” It is the term used to encompass the application of photonics technologies that generate/conserve energy, cut greenhouse gas emissions, reduce pollution, and eventually lead to environmentally sustainable outputs. Photovoltaics, solid-state lighting (SSL), artificial photosynthesis, and energy savings are the prime aspects of green photonics.
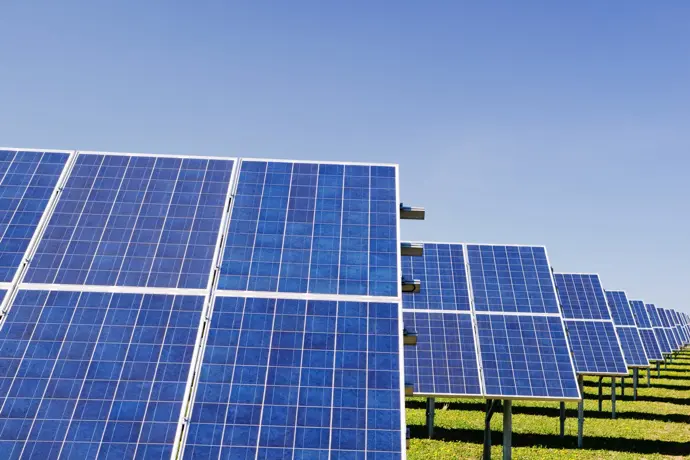
Photovoltaics emerged in 1950 when scientists at the Bell laboratories discovered that silicon doped with certain impurities is very sensitive to light. This technology was later used in solar panels and became a hot topic of research due to its utility as a renewable energy source, reduced carbon emissions, and reduced pollution. Photonics technologies have contributed immensely to improving the efficiency of solar cells. Light trapping has been enhanced multifold by using the photonics concept of spectral sensitivity, angular selectivity, and diffractive gratings.
Solid-state lighting (SSL) technologies such as LEDs (light-emitting diodes) have potential for an improvement over traditional light sources such as incandescent and fluorescent lamps. Philips claims to have developed an LED light bulb that uses one-sixth the energy of a standard 60-watt incandescent bulb. In comparison to Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs), LEDs can save up to six times more energy in a year, have better color refractions, have more longevity, have low power transmission loss, and is difficult to recycle. To further improve these SSL, every week new products are developed globally and new milestones are achieved.
Green photonics is also dealing with the energy consumption due to the fast-growing internet traffic issue. Silicon-based optical interconnects are rapidly replacing the electrical ones. Also, fiber-based lasers are proposed to reduce the manufacturing and maintenance cost. These lasers are claimed to be 15 times more efficient than conventional ones. Green photonics has also opened up a new window of opportunity in the area of environmental sensing. The application of photonics leads to real-time warning in water treatment, whereas standard laboratory tests can take up to 72 hours.
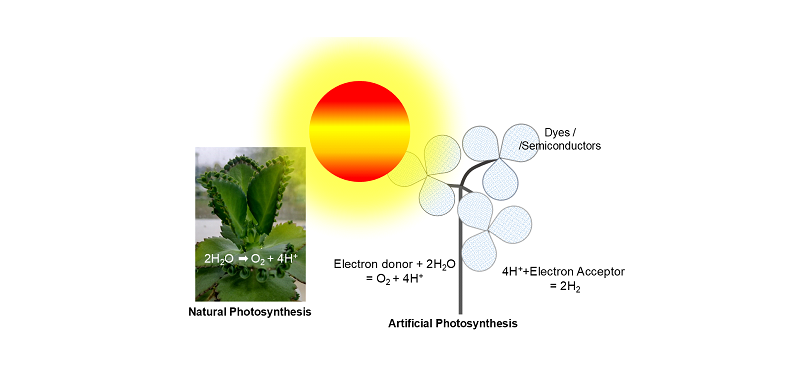
Another very important aspect of green photonics is “artificial photosynthesis.” it is an innovative concept based on synthetic materials to replace chlorophyll molecules and create an artificial leaf.
Power generation from artificial photosynthesis is a green dream beginning to grow tall. The main concept behind this technique is “Ruthenium (Ru) catalyst helps to absorb the light very effectively in the visible spectrum.” Further Rhenium (Re) catalyst is used to actually take the electron produced and knock one of the oxygen molecules off the CO2. The major challenge is ensuring the catalyst is stable and doesn’t degrade over time. Photo-reactive dyes and nanoparticles are suggested to replace chlorophyll.
Sustainability is not only about doing less harm but also about doing better, and green photonics is anticipated to be a key player in the future. It has already been initiated in India; however, the major challenge is its limited knowledge. Optical education is very limited in India. The portion of optics is very short, especially in engineering colleges. The young generation must be trained in optics to implement and deal with photonics technology for a green and beautiful planet.
Author
The author, Dr. Satchi Singh, is a researcher in the field of optics and photonics. She obtained a Ph.D. in Photonics from IIT Guwahati and has taught at the University of Delhi and Central University of Jharkhand as an assistant professor (DST Inspire Faculty).